What Is SRSD? A Step-by-Step Guide for Teachers
Overcoming Challenges with Student Writing Strategies
Writing is one of the most essential skills we teach, but it’s also one of the hardest. Many students don’t know where to start. Others write a few sentences and stop. Even strong readers sometimes freeze when asked to put ideas into words.
Teachers feel the cognitive struggle, too. How do you support a class with many different needs, especially while integrating social-emotional learning, balancing the curriculum, and meeting assessment demands?
There’s a method that works. It’s called Self-Regulated Strategy Development (SRSD).
SRSD is an evidence-based approach that blends two things:
- Writing strategies: step-by-step tools for planning, organizing, and revising.
- Self-regulation skills: goal-setting, self-talk, and monitoring that keep students motivated and in control.
In other words, SRSD teaches both the writing and learning processes. Students gain strategies to structure their writing and self-regulation strategies to manage their motivation, focus, and persistence.
This guide walks you through SRSD as a step-by-step teaching process. By the end, you’ll understand not just what is SRSD, but how to bring it into your classroom in practical, teacher-friendly ways.
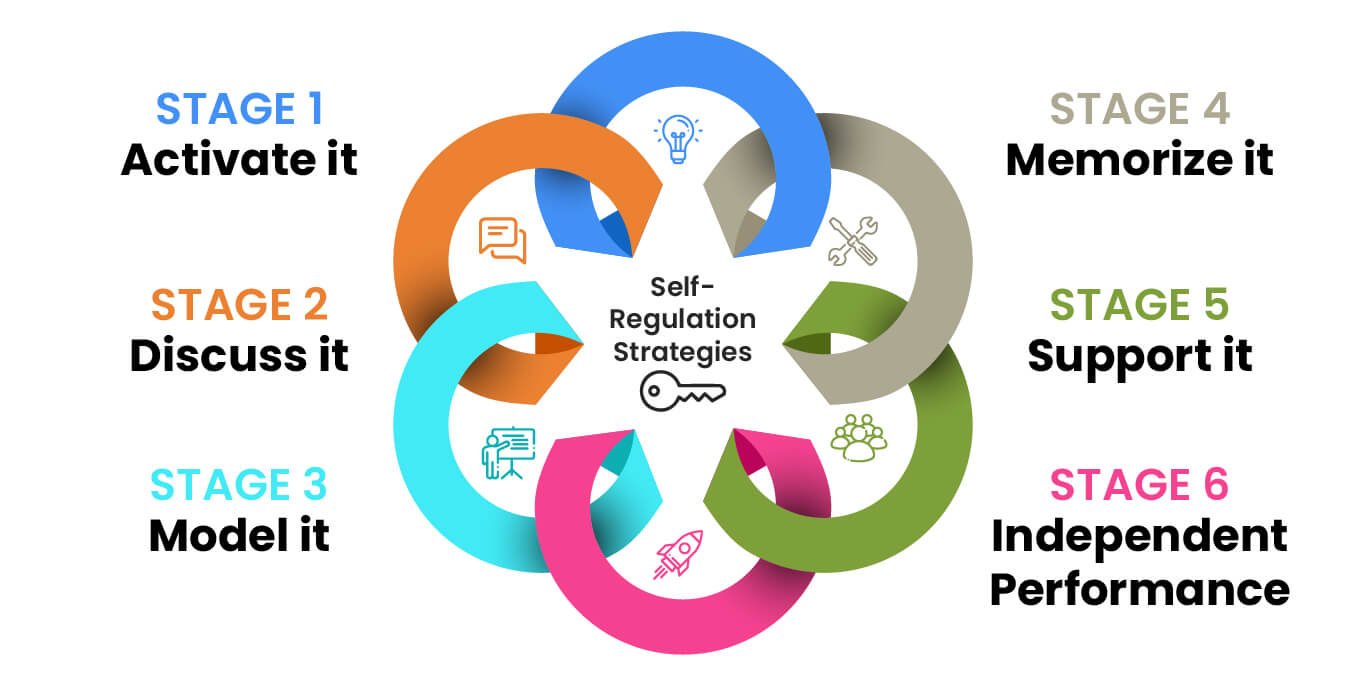
Step 1: Prepare Yourself and Your Students
Preparation is everything before teaching to know what SRSD looks like.. Teachers need to feel confident with the strategies, and students need to understand why they’re learning something new. Think of this stage as laying the foundation for success.
- Learn the strategy yourself. For opinion writing, start with
- TREE (Topic sentence, Reasons, Explain reasons, Ending). For informative writing, try TIDE (Topic, Important details, Describe, Ending). These mnemonics are simple yet powerful. If you’d like extra support, SRSD Online offers courses that walk you through the process step by step.
- Decide where SRSD fits. SRSD works best when woven into what you already teach. Pick a genre you’re covering anyway—opinion essays in grade 3, science reports in grade 5, persuasive writing in middle school. By embedding it into your existing curriculum, you avoid the trap of “one more thing.”
- Set clear expectations. Tell students:
“We’re going to learn a way to make writing easier. These steps will help us plan, draft, and revise without getting stuck.”
These acronyms give students a structure to hold onto, and they’re simple enough that you can model them with ease. If you’d like extra support, SRSD Online offers self-paced, online courses that walk you through the process step by step, making it easier to feel ready before you begin.
Framing SRSD as a tool rather than a rule builds buy-in. Students begin to see writing strategies as supports, not obstacles.
Step 2: Develop Background Knowledge
Students can’t use a writing strategy if they don’t yet understand the basics of the genre. This stage builds the foundation that makes the strategy meaningful.
- Teach key vocabulary. Opinion writing needs terms like topic sentence, reason, detail, and conclusion. Informative writing needs facts, examples, description, and an ending.
- Show strong and weak examples. Compare two short pieces of writing—one organized, one messy. Ask: “Which is easier to understand? Why?” Students quickly see that structure matters.
- Point out text structures in mentor texts. Highlight topic sentences, reasons, and endings in real examples so students see how published writers do it.
📌 Baseline Writing Sample: Before introducing the strategy, ask students to write a quick piece in the target genre with minimal support (e.g., “Should homework be banned?”). This baseline gives you a clear picture of student needs and provides powerful before-and-after evidence of growth.
Teacher Tip: Don’t rush. Students who lack background knowledge will struggle later. A strong foundation here accelerates everything that follows.
Step 3: Discuss It
SRSD isn’t just about skills—it’s also about mindset. Students need to know why the strategy matters and believe it can help them.
- Explain the purpose. Remind students that even professional writers plan before they draft. Strategies aren’t “school tricks”; writers use real tools.
- Set goals together. Help students write specific, personal goals like:
“I will add three reasons to my essay.”
“I will make my ending sum up my opinion.” - Address feelings. Writing is emotional. Ask: “What’s hard about writing for you?” or “When do you feel proud of your writing?” Acknowledge the struggle and show that strategies can make writing less overwhelming.
Why it matters: This step builds self-regulation muscles. Students shift from “writing is hard” to “I have tools to manage it.” That mindset shift is the heart of SRSD.
Step 4: Model It
Modeling is one of the most powerful parts of SRSD. Students need to see what writing looks like in real time.
Explicit Teacher Modeling (“I do”):
- Fill out a graphic organizer step by step.
- Think aloud: “My topic sentence is ‘Pets should be allowed in school.’ My reason is that pets calm kids down. I’ll explain with an example about my dog.”
- Show revision: “Hmm, that sentence doesn’t sound right. I’ll try another way.”
Collaborative Modeling (“We do”):
- Ask students: “What’s a strong topic sentence we could use?”
- Add their ideas to the organizer—even imperfect ones—so they see how writing improves through revision.
- Prompt gently: “We have two reasons. Can anyone suggest a third?”
Why it works: Students first watch you do it, then try it with your support. This two-step modeling lowers the risk of failure, builds confidence, and normalizes writing as a process.
Step 5: Memorize It
For students to own a strategy, they must know it by heart. Memorization builds automaticity, so strategies are available even on a test or when the teacher isn’t there.
- Teach mnemonics clearly. TREE, TIDE, and POW simplify the writing process into steps students can remember.
- Make it playful. Use chants, cheers, or songs: “T-R-E-E, helps me write more easily!”
- Keep it visible. Anchor charts, posters, and sticky notes reinforce memory.
- Build fluency. Give students fun practice with silly prompts like “Should pizza be the school lunch every day?”
Why it matters: When steps are automatic, students free up mental energy to focus on generating ideas, elaborating details, and revising.
Step 6: Support It
Now comes the training wheels phase. Students try the strategy with scaffolds and support.
- Work in pairs or groups to brainstorm and draft.
- Provide prompts: “What’s your topic sentence?” “Do you have three reasons?”
- Give targeted feedback: “Nice job including reasons. Next step- add more detail.”
- Celebrate effort and persistence, not just finished work.
Why it matters: This is where strategy use and self-regulation blend. Students monitor progress, use self-talk, and rely on prompts as temporary supports. Over time, scaffolds fade, but only at the pace students are ready for.
Step 7: Independent Performance
This is the goal of SRSD students writing independently with strategies and self-regulation tools in place.
- They plan, draft, and revise without teacher cues.
- They use checklists and self-talk naturally.
- They monitor their own goals: “Did I include three reasons?”
- They reflect afterward: “What worked well? What will I try differently?”
Why it matters: Students no longer see writing as mysterious or overwhelming. They view it as a process they can manage. Independence builds confidence and transfers across subjects.
Step 8: Monitor and Reflect
SRSD isn’t a one-and-done program. The final step is creating a cycle of assessment and reflection that sustains growth.
- Review student samples regularly, not just at the end of a unit.
- Teach students to use rubrics for self-assessment.
- Guide reflection: “Did the strategy help you? Where did you get stuck?”
- Reset goals for the next piece.
Why it matters: Monitoring and reflection prevent strategies from fading away. Students see evidence of growth, teachers spot areas for extra support, and writing improvement becomes a continuous journey.
Bringing It All Together
Here’s how SRSD might look in practice over 6–8 weeks for Grade 5 opinion writing:
- Develop Background Knowledge: Review genre features, read mentor texts.
- Discuss It: Discuss why planning matters, and chart what’s hard about writing.
- Model It: Teacher thinks aloud and demonstrates TREE.
- Memorize It: Practice TREE with chants, posters, and fun prompts.
- Support It: Students plan and draft with partners, teacher prompts as needed.
- Independent Performance: Students apply TREE independently while the teacher confers.
- Monitor & Reflect: Students assess their work, set new goals, and celebrate progress.
Why This Step-by-Step Approach Works
- Reduces overwhelm. Writing feels manageable because it’s broken into steps.
- Builds confidence. Students see tangible progress in their writing.
- Teaches independence. SRSD scaffolds fade until students are self-regulated.
- Evidence-based. Decades of research show SRSD works across grades, subjects, and populations, including struggling writers and students with disabilities.
Tips for Success
- Start small: pick one genre and one strategy.
- Model more than you think you need.
- Use kid-friendly language and mnemonics.
- Celebrate small wins to build motivation.
- Be flexible: loop back to earlier steps if students need more support.
Final Thoughts
So, what is SRSD? It’s more than a writing program. It’s an instructional framework combining explicit writing strategies with self-regulation tools so students can write confidently and independently.
For teachers, SRSD provides a clear, structured path: start with background knowledge, build buy-in, model and memorize strategies, support practice, then watch students take off independently while continuing to reflect and reset goals.
For students, SRSD builds more than essays. It develops motivation, resilience, and the belief that they can succeed as writers. That’s why schools worldwide are adopting SRSD as part of their educational framework.
And if you’d like extra support, SRSD Online offers self-paced courses that walk you through every stage, step by step so you can feel ready to launch SRSD in your own classroom.

About the Author
Randy Barth is CEO of SRSD Online, which innovates evidence-based writing instruction grounded in the Science of Writing for educators. Randy is dedicated to preserving the legacies of SRSD creator Karen Harris and renowned writing researcher Steve Graham to make SRSD a standard practice in today’s classrooms. For more information on SRSD, schedule a risk-free consultation with Randy using this link: Schedule a time to talk SRSD.