IES Reviews the Science of Writing - Free Reports
The US INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION SCIENCES recommends SRSD on the What Works Clearing house website.

IES Blog: The Science Behind Self-Regulated Strategy Development:
Inside IES Research, June 16, 2022
Improving Academic Achievement through Instruction in Self-Regulated Strategy Development: The Science Behind the Practice Dr. Karen Harris describes developing SRSD and the research behind it. Self-Regulated Strategy Development (SRSD) is...
Improving Academic Achievement through Instruction in Self-Regulated Strategy Development: The Science Behind the Practice
Dr. Karen Harris describes developing SRSD and the research behind it. Self-Regulated Strategy Development (SRSD) is an evidence-based instructional approach characterized by active, discussion-based, scaffolded, and explicit learning of knowledge of the writing process; general and genre-specific knowledge; academic vocabulary; and validated strategies for teaching reading and writing. IES has supported multiple research studies on SRSD for students with learning disabilities in K-12 and postsecondary general education settings. SRSD is used in as many as 10,000 classrooms across the United States and in 12 other countries. In this interview blog, we spoke with Dr. Karen Harris, the developer of SRSD, to learn more about this effective instructional strategy, the IES research behind it, and next steps for further scaling of SRSD so that more students can benefit.
What Works Clearinghouse Intervention Report: Self-Regulated Strategy Development
Steve Graham, Karen Harris et al. (2017)
IES recommends SRSD as an effective intervention. When downloading the “Self-Regulated Strategy Development (SRSD) Intervention Report,” you will access a detailed guide on an effective teaching method designed to improve...
IES recommends SRSD as an effective intervention.
When downloading the “Self-Regulated Strategy Development (SRSD) Intervention Report,” you will access a detailed guide on an effective teaching method designed to improve students’ academic skills. This report outlines a six-step process that starts with teacher-led instruction and progresses to students independently applying strategies such as planning and organizing their ideas before writing. The six steps include providing background knowledge, discussing, modeling, memorizing, supporting, and independently performing the strategy. Additionally, the report emphasizes teaching self-regulation skills like goal-setting and self-monitoring. The SRSD model is adaptable, allowing steps to be combined, reordered, or repeated based on student needs, and can be used with students in grades 2 through 12 in various settings. The report also includes a comprehensive research summary showing SRSD’s positive effects on writing achievement. It provides an overview of the intervention, research details, outcome measures, and effectiveness ratings, making it a valuable resource for improving writing instruction in diverse educational environments.
Here is a table from the What Works Clearinghouse report:
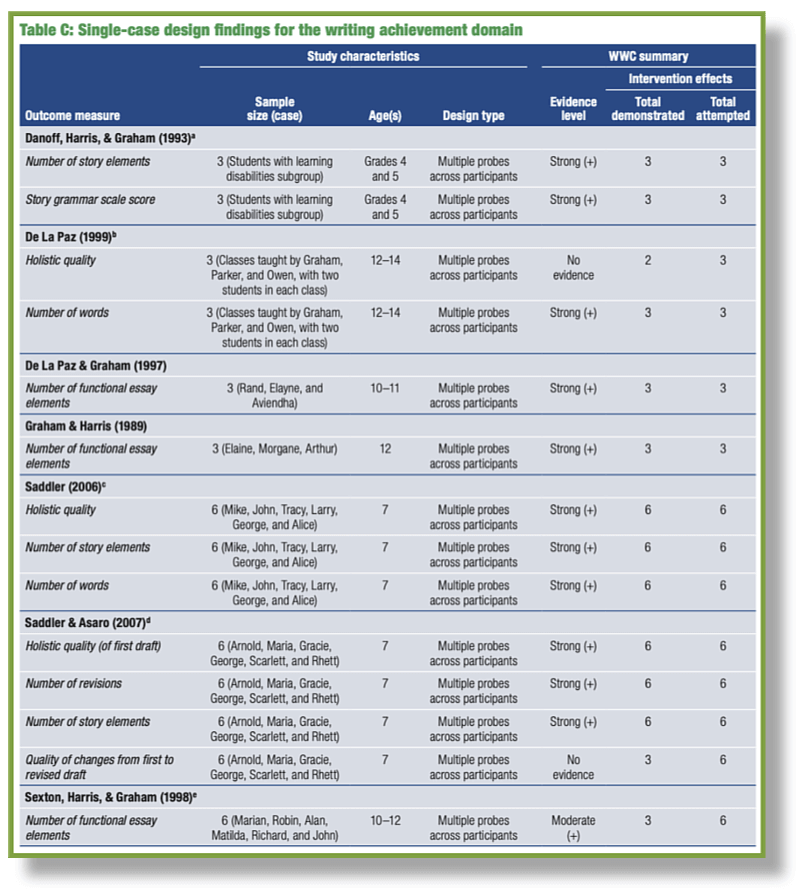
This chart presents findings from various single-case design studies on the effectiveness of Self-Regulated Strategy Development (SRSD) in improving writing achievement for students with learning disabilities. In summary, SRSD is an effective intervention for improving various aspects of writing for students with learning disabilities. Multiple studies show strong positive effects, indicating that SRSD is a robust and broadly applicable approach. It positively impacts a wide range of writing skills, from story structure to overall quality and length of texts. The consistent positive outcomes across different age groups and settings reinforce the reliability and validity of SRSD as an effective instructional method. The chart strongly supports these conclusions, demonstrating the consistent and significant benefits of SRSD for enhancing writing achievement.

IES Practice Guide: Teaching Elementary School Students to Be Effective Writers
Steve Graham et al. (2012)
When downloading the “Educator’s Practice Guide: What Works Clearinghouse – Teaching Secondary Students to Write Effectively,” you receive a detailed and structured resource designed to tackle classroom and school challenges...
When downloading the “Educator’s Practice Guide: What Works Clearinghouse – Teaching Secondary Students to Write Effectively,” you receive a detailed and structured resource designed to tackle classroom and school challenges in teaching writing. The guide starts with an introduction that sets the context for the recommendations. The first recommendation focuses on explicitly teaching appropriate writing strategies using a Model-Practice-Reflect instructional cycle. This is further broken down into teaching strategies explicitly and utilizing the instructional cycle to reinforce them. The second recommendation emphasizes integrating writing and reading to highlight key writing features. The third recommendation advises using assessments of student writing to inform instruction and provide feedback. Additional sections include a glossary, a postscript from the Institute of Education Sciences, information about the authors, disclosure of potential conflicts of interest, and a rationale for evidence ratings. The guide concludes with comprehensive references and endnotes, ensuring I have a robust framework to effectively enhance my students’ writing skills.

IES Practice Guide: Teaching Secondary Students to Write Effectively
Steve Graham et al. (2012)
When downloading the “Educator’s Practice Guide: What Works Clearinghouse – Teaching Secondary Students to Write Effectively,” You will receive a detailed and structured resource designed to tackle classroom and school...
When downloading the “Educator’s Practice Guide: What Works Clearinghouse – Teaching Secondary Students to Write Effectively,” You will receive a detailed and structured resource designed to tackle classroom and school challenges in teaching writing. The guide starts with an introduction that sets the context for the recommendations. The first recommendation focuses on explicitly teaching appropriate writing strategies using a Model-Practice-Reflect instructional cycle. This is further broken down into teaching strategies explicitly and utilizing the instructional cycle to reinforce them. The second recommendation emphasizes integrating writing and reading to highlight key writing features. The third recommendation advises using assessments of student writing to inform instruction and provide feedback. Additional sections include a glossary, a postscript from the Institute of Education Sciences, information about the authors, disclosure of potential conflicts of interest, and a rationale for evidence ratings. The guide concludes with comprehensive references and endnotes, ensuring you have a robust framework to effectively enhance your students’ writing skills for teaching writing to secondary school students. It includes detailed, step-by-step instructions on implementing these strategies in the classroom, real-world examples, and tips for overcoming common challenges. The guide also provides a wealth of supplementary materials, such as lesson plans, writing prompts, and assessment tools to help teachers effectively foster their students’ writing skills. Additionally, it includes insights into creating a positive writing environment and encouraging student engagement and motivation in writing activities.

Fixing our National Writing Crisis
Steve Graham (2015)
It all Starts Here: Fixing our National Writing Crisis From the Foundation Teachers will find specific strategies for effective writing instruction, such as providing...
It all Starts Here:
Fixing our National Writing Crisis From the Foundation
Teachers will find specific strategies for effective writing instruction, such as providing ample writing practice, using frequent assessments to inform instruction, explicitly teaching writing processes and strategies, and integrating writing across the curriculum. This resource aims to equip educators with the knowledge and tools to address and resolve the national writing crisis by strengthening writing instruction at all grade levels.
This white paper, “It All Starts Here: Fixing Our National Writing Crisis from the Foundation” by Steve Graham, Ed.D., is an in-depth analysis of the state of writing education in the United States and practical recommendations for improvement. This document addresses the alarming decline in writing proficiency among students, as evidenced by low SAT and NAEP scores. It emphasizes the critical need for foundational writing skills from early grades to ensure students are prepared for the demands of higher education and the modern workforce. This white paper includes detailed discussions on the importance of writing, the impact of writing on academic success, and the evolving requirements of the 21st-century workplace. The white paper underscores the importance of a positive writing environment and the role of technology in writing instruction.

Writing Next: Effective Strategies to Improve Writing of Adolescents
Graham & Perin (2007)
When downloading the study “Writing Next: Effective Strategies to Improve Writing of Adolescents in Middle and High Schools” by Steve Graham and Dolores Perin, you receive a comprehensive report that...
When downloading the study “Writing Next: Effective Strategies to Improve Writing of Adolescents in Middle and High Schools” by Steve Graham and Dolores Perin, you receive a comprehensive report that enhances writing instruction for adolescents through empirical evidence-based recommendations. Commissioned by the Carnegie Corporation, this influential report synthesizes research to identify 11 key elements of effective writing instruction using a meta-analysis of experimental and quasi-experimental studies. These elements include writing strategies, summarization, collaborative writing, specific product goals, word processing, sentence-combining, prewriting, inquiry activities, the process writing approach, the study of models, and writing for content learning. The guide provides an executive summary, detailed implementation recommendations, and appendices detailing the meta-analysis methodology and supporting studies. It highlights the need for all students, especially struggling writers, to become proficient and flexible writers, stimulating policy and research discussions to improve literacy nationwide.

Effective Writing Instruction for All Students
Steve Graham (2008)
When you download “Effective Writing Instruction for All Students” by Steve Graham, you receive a comprehensive guide designed to enhance writing instruction across grade levels. Written for Renaissance Learning, this...
When you download “Effective Writing Instruction for All Students” by Steve Graham, you receive a comprehensive guide designed to enhance writing instruction across grade levels. Written for Renaissance Learning, this publication offers seven evidence-based recommendations to improve students’ writing skills. These include dedicating time to writing across the curriculum, increasing students’ knowledge about writing, fostering their interest and motivation, helping them become strategic writers, teaching basic writing skills to mastery, leveraging technological tools, and using assessments to gauge progress and needs. The guide is grounded in scientific studies and practical teaching strategies, providing teachers with actionable steps to implement effective writing practices in their classrooms. It also emphasizes the importance of consistent and sustained writing instruction to ensure students become proficient writers from early grades through high school. By downloading this report, teachers gain valuable insights and tools to support all students, including those with learning difficulties, ultimately enhancing their academic performance and literacy skills.